Ok. This post is an SEO topic. If you’re not interested and tired of hearing tips from me on optimizing keywords, go away! Just come back on other days, when I’m in the mood blogging about more interesting topics. You are not required to read this blog anyway.
Now, let’s start.
Google has this definition of the allintitle: operator:
If you start a query with [allintitle:], Google will restrict the results to those with all of the query words in the title. For instance, [allintitle: google search] will return only documents that have both “google” and “search” in the title. {Source}
What it actually does is that it will only search for web pages that has those keywords in the title tag. That is, between the <title></title> when you view the HTML source.
This information is useful when you are trying to size-up the competition. For example: if you search for how to make a baby, you will get a whopping 400+ million results.
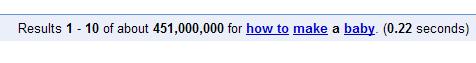
But if you search for allintitle:how to make a baby, you will only get around 4000+ results.
What does this mean? It means that although there are 400+ million web pages mentioning the keywords how to make a baby, only 4000+ of them are using those keywords on the title tag. So what? It means a lot to me. It means that only 4000+ web pages are actually optimizing for that keywords, because if a person knows SEO, he will not miss putting his keywords on the title tag. Right?
It means that although at first, it seems that I’ll be competing with 400+ million web pages, majority of them are not optimized well. Only 4000+ pages are using it on the title tag. Giving me a fat chance of hitting the first page in less time.
So if you think I’m crazy trying to optimize how to make a baby because there are 400+ million competitors, think again. My previous post actually is already on the 4th page out of 400+ million results. 🙂 And is still slowly moving up.








nice share 😀 hehehe.. binasa ko from start to finish 😀
di ko nalang binasa kasi pinapaalis ako eh. hehe joke. thanks for sharing!!!
Good read! Yet another great tip for aspiring SEO slaves este master. 😀
I tried the allintitle with your keyword; wala ka na sa 4th or the 3rd or the 2nd… 🙁
@Ron Del Rosario… kanina, andyan pa yan eh. googling “how to make a baby site:macuha.com”, wala rin sya sa result. meaning, wala sya sa index ng Google ngayon. babalik din yan bukas. 😀
astig! salamat sa tips, i’ll try this asap… 😉
Doesn’t help me at all… 😉
Just changed my blog template, have to get my keyword in there, you made me notice that. Thanks!
I’ll be using this in the future. Simple easy tip.
So that is why your making post not relevant to SEO. You are just targeting popular keywords. Anyway thanks for this valuable info.
I think the first paragraph was directed at me since I complained that the blogger speaks nothing but hijacking keywords to lure people in to earn more.
There’s nothing wrong in that, we all want to earn something in the end BUT repetitively saying you’re gonna take advantage of keywords just for that before discuss the topic takes the post quality a few notches down (alot, actually, since I can see the green of your eyes.) I just want to read a post about Halloween without reading that the poster earned big last valentines for his valentines post and that he hijacked this and that keywords for that purpose alone. Its like the showbiz section of the evening news talking about a celebrity’s nonsense just to boost interest in promoting their shows.
I didn’t say stop talking about SEO and keywords related topics. After all, why would I complain if it IS the topic.
@Napolexander Santiago… oh well. that’s just my style since I started this blog. i used to teach people by example, showing what keywords I’m hijacking and the results afterwards. well, i cannot please everybody, anyway. thanks for you input though.
Thanks for this great article.
I have now gone and adjusted the title tags in all of my pages to make sure they are targetting what I need them to. I dint know about this allintitle trick.
thanks again
Now optimising for some keywords doesnt seem so difficult
thanks
Gerard
@Marhgil
Yes, that is my comment and I understand it is your style. I’m just one of those unfortunate enough to speak my mind and gets in trouble for it. Anyways, that’s how it appears to me.. All I’m saying is there’s a right place for everything. That’s that..mums the word.
Anyway, I tried your tip about allintitle and it sure did made my searches a bit easier since I’m one of those that do searches alot in a day..I’m a trivia and statistics geek.
And I’ll sure keep that in mind once I’m done restructuring my own amateur blog..yeah
does it apply in blogger?
I just write and publish my posts. How do I put the keyword in the title tag? pasensya na medyo di ako marunong sa mga ganito..
Please do you have advices on how i can get back to the SERP. bigla kasi akong nawala sa SERP eh. Traffic is down to 200 UVS instead of 2K UVS..
thanks
Thanks for this post. I knew there was a way to search other than just typing in the words and searching in quotes, but I couldn’t remember what it was. I’ll try the allintitle: for some of the keywords in my niches.
Great tip. I have discovered many keywords in my niche with very little competition based on the “allintitle:” query. Keep them coming!!
Haha, nice tip there!
That’s a great tip. I often forget to consider keywords in my blog and just write about what I want.
I used that when sizing up competition and looking for good names for my fly fishing for stripers site. I need to remember to use this more often, not just when picking domain names and sizing up competition
Very useful — yeah, I know it, but need to remember to do this more often.
I’ve forgotten so many google tricks — need to rite them all down!
Wow
Nice tip
nice tip but I’m not sure what it really means in the end. OK, so now I have only say 4,000+ sites that are using the same text in their title, but how does that help me in ensuring I get to the first page of Google?
I used that when sizing up competition and looking for good names for my fly fishing for stripers site. I need to remember to use this more often, not just when picking domain names and sizing up competition